In the veterinary culture of English-speaking countries, it is common to use acronyms for all kinds of medical terminology. In other countries the use of these acronyms is not so widespread, so it is normal for foreign veterinarians starting to work in the United Kingdom to be surprised by the number of abbreviations that are used and that we have never heard of! Below is an extensive list of acronyms that are used commonly in practice and that you should become familiar with.Â
Food and drug administration
Ad lib ad libitum
CRIÂ constant rate infusion
NPOÂ nothing by mouth (nil per os)
TPNÂ total parenteral nutrition
Administration Routes
POÂ oral(ly) (per os)
SCÂ subcuteneous(ly(Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â
IMÂ intramuscular(ly)
IVÂ intravenously)
Frequency of administration
sid once a day (q24h)
bid twice a day (q12h)
tid three times a day (q8h)           Â
qid four times a day (q6h)
eod every other day (q48h)
prn as needed (pro re nata)
History and physical exam
C+ cough Dx diagnosis Tx treatment
D+ diarrhoea Ddx differential diagnosis C/U check up
V+ vomiting Hx history RV revisit
Fx fracture Px prognosis O owner
Vx vaccine Sx surgery (en algunos sitios lo usan para symptoms)
BARÂ bright, alert and responsive
QAR quiet, alert and responsive        Â
TPR temperature, pulse, respirations    Â
HRÂ heart rate
RRÂ respiratory rate
bpm beats per minute
rpm respirations per minute
MMÂ mucous membranes
BWÂ bodyweight
BCS body condition score             Â
S/O stitches out, sutures out          Â
PEÂ physical exploration, physical exam
INBÂ if not betterÂ
PLR pupillary light reflex              Â
BIOP been in owner’s possession
STO spoke to the owner    Â
DLHÂ domestic long hair (cat)Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â
DSHÂ domestic short hair (cat)Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â Â
EAGs empty anal glands
NADÂ nothing abnormal detected (a veces se ve como NAF-no abnormal findings)
WNLÂ within normal limits
VMIÂ very much improved
SOAPÂ signalment, objective, assessment, plan (a method of organising medical records)

This dog presented collapsed, he had pale MM, a HR of 140bpm and a BP of 89/45mmHg. An AFAST revealed an haemoabdomen and a splenic mass (Image by wirestock on Freepik)
Cardiorespiratory
AVÂ block atrioventricular block
BPÂ blood pressure
CHFÂ congestive heart failure
DCMÂ dilated cardiomyopathy
HCMÂ hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
URIÂ upper respiratory infection
URTIÂ upper respiratory tract infection
Neurology and musculoskeletal
CNSÂ central nervous system
CrCLÂ cranial cruciate ligament
CSFÂ cerebrospinal fluid
DJDÂ degenerative joint disease
IVDDÂ intervertebral disk disease
OAÂ osteoarthritis
TMJÂ temporomandibular joint
Urogenital
FLUTDÂ feline lower urinary tract diseaseÂ
FUSÂ feline urologic syndrome
GFRÂ glomerular filtration rateÂ
AIÂ artificial insemination
BUNÂ blood urea nitrogen
UTIÂ urinary tract infection
Gastrointestinal
EPIÂ exocrine pancreatic insufficiency
GDVÂ gastric dilatation-volvulus
GIÂ gastrointestinal

Few things are beyond the scope of acronyms in the veterinary prac8ces of the UK. Acronyms are even used for breeds, such as this CKCS. Abbreviations are also used for many other breeds, such as the West Highland WhiteTerrier (westie-WHWT), the Yorkshire Terrier (yorkie), the Cavalier King Charles Spaniel (cavie) or the Staffordshire Terrier (staffie).
Infectious diseases
FIPÂ feline infectious peritonitis
FIVÂ feline immunodeficiency virus
KCÂ kennel cough
TBÂ tuberculosis
Emergency and critical care
CPRÂ cardiopulmonary resuscitation
DNRÂ do not resuscitate
DOAÂ dead on arrival
ICUÂ intensive care unit
PTSÂ put to sleep
QOLÂ quality of life
RTAÂ road traffic accident
OOHÂ out of hours (trabajo fuera del horario normal de abertura de la clÃnica)
Diagnostic techniques
BALÂ bronchoalveolar lavageÂ
BASTÂ bile acid stimulation test
BGÂ blood glucose
CBCÂ complete blood count
DTMÂ dermatophyte test medium
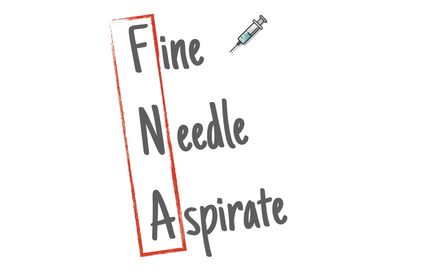
FNAÂ fine needle aspirate
RBCÂ red blood cells
MRIÂ magnetic resonance imagingÂ
CTscan- computed tomography
ECGÂ electrocardiogram/electrocardiography.Â
PCVÂ packed cell volume (hematocrito).Â
UAÂ urinalysis
U/S ultrasound. También como US
POCUS- point of care ultrasound
AFASTÂ abdominal focused assessment sonography for trauma, tiage and tracking
TFASTÂ thoracic focused assessment sonography for trauma, tiage and tracking
 X-ray radiograph
WBC white blood cells. Se puede añadir una “C†para indicar
recuento (count), es decir, WBCC (y también RBCC)
Veterinary profession
CPDÂ continuing professional development
RSPCAÂ Royal Society for the Prevention of Cruelty in Animals
RCVSÂ Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons
MRCVSÂ member of the Royal College of Veterinary Surgeons
DVM Doctor of Veterinary Medicine. Es la denominación oficial que se da en Reino Unido a un veterinario graduado en España.
Potpourri
Abs/Abx antibiotic(s)
ACTHÂ adrenocorticotropic hormone
DICÂ disseminated intravascular coagulation
KCSÂ keratoconjunctivitis sicca
DMÂ diabetes mellitus
IUÂ international units
NSAID(s)Â nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug(s)
